Argo Group is a global specialty insurer, and as such as we have deep expertise in evaluating and pricing risks. Risk awareness is of critical importance to our success as a business, and therefore Argo has established a simple but powerful Vision for Risk Management that we have communicated to our employees and stakeholders.
“Risk intelligence enables Argo to achieve its strategic objectives by taking appropriate risks and exploiting opportunities.”
RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
Argo has developed and implemented an enterprise risk management framework (ERM) over a number of years to help bring together all the elements required to manage risk effectively across the organization. The diagram below is an articulation of the five key elements of the framework.
Argo’s Risk Management Framework
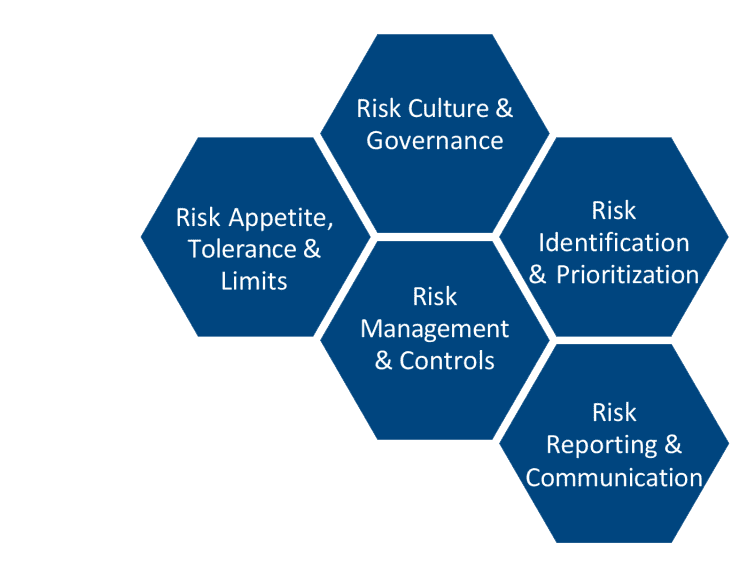
ERM Chart
Argo’s Enterprise Risk Management strategy consists of driving the continuous maturing of the ERM framework in line with International Standard ISO 31000 (2018) by ensuring that this approach is adopted in our day-to-day decision-making and informs our risk-reward choices in a very practical way.
The aim is to create an organization where all staff have access to the appropriate tools, processes and training to enable them to make informed and timely risk-taking decisions. This implies that:
• Risks are made visible.
• Risks are discussed and understood.
• Risks are owned.
• Appropriate action is taken.
• Argo learns from its risk-taking.
ERM is supported at all levels in the organization but led from the top. Argo has a Board-approved Risk Management Policy, which defines the overall approach to enterprise risk management for the organization and sets the context for the framework. View the Risk Management Policy (PDF).
The Risk Management Function (RMF) has a formal Board Risk & Capital Committee approved charter which outlines is role, responsibility and authority as a second line of defense function including its role in coordinating Argo Group’s Sustainability program. View the Risk Management Function Charter (PDF).
In October 2020 Standard & Poor’s (S&P) confirmed in their annual rating report its view of ERM at Argo Group:
“Over the past few years, Argo has made strides to enhance its enterprise risk management framework, advance its risk control functions, and embed its processes into its strategic planning. The company places greater emphasis on data analytics and has been increasing the use of its economic capital model as an additional tool when making key business decisions.”
The Five Principles of Risk
Argo Group takes risks in pursuit of reward. It relies on a formal process – Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) – to identify, assess, monitor, manage and report risks. ERM builds risk intelligence and conveys the skills and insight needed to take appropriate risks, exploit opportunities and achieve strategic objectives. ERM is underpinned by five key principles and the processes set out in Argo’s risk management framework.
1. Risks are owned.
Argo assigns accountability for managing risks within the framework set out by the board.
Risk culture and governance
Governance provides the authority to assign and oversee responsibility for ownership and management of risk. Risk culture refers to the shared values that guide Argo to do what is right for the company and its clients when taking risks.
2. Risks are visible.
Risks are visually communicated in a way that helps Argo determine the potential impact on particular business strategies or processes.
Risk identification and prioritization
Argo’s Risk Assessment Process (RAP) captures and categorizes risks to build a clear understanding of threats and opportunities, and to help prioritize actions.
3. Risks are discussed and understood.
With risks owned and visible, Argo can lead open, in-depth discussion to better understand risk and make informed decisions about the type and amount of risk to take.
Risk appetite, tolerance and limits
Argo makes decisions about risk based on:
• Appetite – the risk exposure considered acceptable to achieve objectives
• Tolerance – the specific level of risk that Argo is prepared to bear for specific risks
• Limits – practical controls that help keep risk within tolerances
4. Appropriate action is taken.
Armed with the knowledge needed to make effective risk decisions, Argo is able to enact the controls necessary to manage risk within the defined appetite, tolerance and limits.
Risk management and controls
ERM equips Argo to make swift and informed choices in response to threats and opportunities. Risk responses fall into five categories: reduce the risk, accept the risk as is, substitute for lower risk, transfer or share the risk, or avoid the risk.
5. Argo Group learns from taking risks.
Risk management is an iterative and dynamic discipline within a constantly changing risk landscape. The goal is to create an agile and resilient organization that continually adapts the practice of risk management while minimizing threats and maximizing opportunities.
Risk reporting and communication
Argo strives to raise risk awareness and reinforce the sound management of risk through a culture of learning, openness and communication. The company encourages disclosure of near misses and loss events as part of that learning process. Risks are reported internally and externally to provide assurance that key risks are managed effectively.




